[Git] Git Submodule 사용 방법
회사에서 진행하던 프로젝트에 Git Submodule을 적용해 볼 수 있지 않을까 생각이 들어 공부한 내용을 기록하고자 한다.
개요
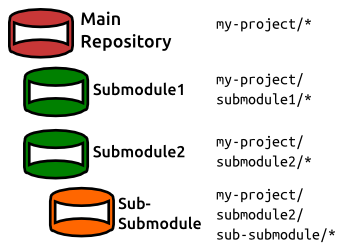
Git Submodule이란, Git 저장소 안(하위)에 디렉토리로 분리해 넣은 또 다른 Git 저장소이다.
- 상위 저장소: main repository
- 디렉토리로 분리되어 들어간 하위 저장소: submodule
프로젝트에서 다른 프로젝트를 함께 사용해야 하는 경우를 위해 Git에서 제공하는 기능이다. 외부에서 개발한 라이브러리나, 내부 여러 프로젝트에서 공통으로 사용할 라이브러리 코드를 관리하고 동기화할 필요가 있을 때 주로 사용한다.
이 때, main repository와 submodule은 각각 독립적인 프로젝트로 관리된다. 따라서 두 저장소의 커밋은 동기화되지 않고, 별도로 관리된다. 이것은 submodule의 내용이 변경되더라도 main repository에서 이 내용이 자동으로 업데이트되지 않음을 의미한다. main repository에서 submodule의 상태를 확인하고, 업데이트해야 한다.
부모 자식 간의 관계로 생각해 main repository에서 submodule의 커밋까지 다 관리할 것이라고 생각하면 착각이다. main repository와 submodule이 연결된 것은 맞지만, main repository에서는 submodule의 커밋 로그를 바탕으로, submodule 데이터를 가져와 사용할 뿐이다.
결과적으로, 서로 다른 두 프로젝트를 별개의 Git으로 관리하면서도, 그 중 하나를 다른 프로젝트에서 사용할 수 있게 된다.
.gitmodules
main repository에서 submodule을 사용하고자 할 때, submodule 각각의 프로젝트 정보를 담고 있는 설정 파일이다.
아래와 같은 항목으로 구성된다.
[submodule "DbConnector"]
path = DbConnector
url = https://github.com/chaconinc/DbConnector
여러 가지 설정 항목이 있지만, 그 중에서도 주로 사용하게 되는 설정 항목은 다음과 같다.
main repository에서 사용할 submodule의 개수만큼 위 설정 항목이 추가되며, .gitignore 파일처럼 버전 관리의 대상이 된다. 따라서 main repository 프로젝트를 clone하는 사람은 이 파일을 통해 해당 프로젝트에서 사용하는 submodule이 어떤 것이 있는지 확인할 수 있다.
사용
main repository, submodule을 사용하는 예시 상황을 가정하기 위해, 아래와 같이 2개의 Git Repository를 생성한다.
-
main-repo: main repository$ mkdir main-repo $ cd main-repo $ echo "#main-repo" >> README.md $ git init $ git add . $ git remote add origin https://github.com/sirzzang/main-repo.git $ git push origin master -
submodule-repo: submodule repository$ mkdir submodule-repo $ cd submodule-repo $ echo "#submodule-repo" >> README.md $ git init $ git add . $ git remote add origin https://github.com/sirzzang/submodule-repo.git $ git push origin master
Submodule을 Project에 추가
main repository에 submodule을 추가하기 위해서는 git submodule add 커맨드를 이용한다.
git submodule add <repo-url> [path]
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git submodule add git@github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo.git
Cloning into '/home/eraser/temp/submodule-test/main-repo/submodule-repo'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (3/3), done.
추가 후, main repository의 상태를 확인해 보면, 아래와 같이 .gitmodules와 submodule에 해당하는 디렉토리 submodule-repo/가 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git status
On branch master
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master'.
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
new file: .gitmodules
new file: submodule-repo
-
git diff커맨드를 통해 달라진 내용을 확인한 결과eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git diff --cached submodule-repo diff --git a/submodule-repo b/submodule-repo new file mode 160000 index 0000000..ea76cfc --- /dev/null +++ b/submodule-repo @@ -0,0 +1 @@ +Subproject commit ea76cfc7e1e8e8d8899ec0fc53401499a9505802 -
--submodule옵션을 주면, 더 자세히 확인 가능eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git diff --cached --submodule diff --git a/.gitmodules b/.gitmodules new file mode 100644 index 0000000..5c36d60 --- /dev/null +++ b/.gitmodules @@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ +[submodule "submodule-repo"] + path = submodule-repo + url = git@github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo.git Submodule submodule-repo 0000000...ea76cfc (new submodule)
main repository에 submodule을 추가하게 될 경우, submodule에 해당하는 디렉토리 전체가 하나의 특별한 커밋으로 취급된다. 해당 디렉토리에 대한 git mode는 160000이다.
이렇게 main repository에 submodule을 추가하면, main repository는 submodule의 특정 커밋을 가리키게 된다. 이제 submodule을 포함한 커밋을 생성하면, main repository에서의 submodule 추가가 완료된다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git add .
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git commit -m 'add submodule-repo as a submodule'
[master 9faed64] add submodule-repo as a submodule
2 files changed, 4 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 .gitmodules
create mode 160000 submodule-repo
main repository 원격 저장소에 push하면, 아래와 같이 submodule이 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다. submodule 뒤에 커밋 해시 값이 붙어 있는 것도 확인할 수 있다.
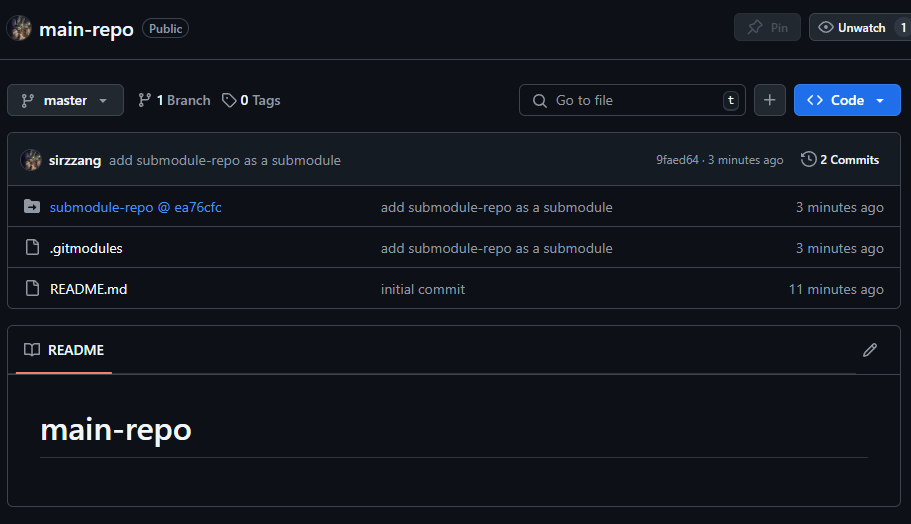
만약 submodule 저장소에 대한 접근 권한이 없는 사용자가 있다면, main repository에서 submodule 링크를 클릭해도 이동할 수 없다.
Submodule을 포함한 Project Clone
submodule을 포함하고 있는 프로젝트를 사용하고자 할 경우 어떻게 해야 할까. submodule을 포함하고 있는 main repository를 최초로 clone할 때, 기본적으로 submodule에 해당하는 디렉토리는 비어 있다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp$ git clone git@github.com:sirzzang/main-repo.git
Cloning into 'main-repo'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 6, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (6/6), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Total 6 (delta 0), reused 6 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (6/6), done.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp$ cd main-repo/
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo$ ls -al
total 24
drwxrwxr-x 4 eraser eraser 4096 Nov 26 06:52 .
drwxrwxr-x 10 eraser eraser 4096 Nov 26 06:52 ..
drwxrwxr-x 8 eraser eraser 4096 Nov 26 06:52 .git
-rw-rw-r-- 1 eraser eraser 102 Nov 26 06:52 .gitmodules
-rw-rw-r-- 1 eraser eraser 12 Nov 26 06:52 README.md
drwxrwxr-x 2 eraser eraser 4096 Nov 26 06:52 submodule-repo
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo$ ls -al submodule-repo
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 eraser eraser 4096 Nov 26 06:52 .
drwxrwxr-x 4 eraser eraser 4096 Nov 26 06:52 ..
서브 모듈을 포함한 디렉토리를 사용하기 위해서는 두 가지 단계를 거쳐야 한다.
- submodule 초기화:
git submodule init - submodule 업데이트:
git submodule update
그게 귀찮다면, clone 시 --recurse-submodules 옵션을 주면 된다.
git clone --recurse-submodules
init
clone한 main repository에서 git submodule init 커맨드를 실행한다. Git이 submodule 설정 정보를 바탕으로 로컬 환경 설정 정보를 준비하게 된다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo$ git submodule init
Submodule 'submodule-repo' (git@github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo.git) registered for path 'submodule-repo'
update
git submodule update 커맨드를 실행한다. Git이 submodule 원격 저장소 상태를 바탕으로, 로컬 저장소 submodule 상태를 업데이트한다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo$ git submodule update
Cloning into '/home/eraser/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo'...
Submodule path 'submodule-repo': checked out 'ea76cfc7e1e8e8d8899ec0fc53401499a9505802'
실행 결과를 통해 어떤 일이 일어나는지 확인해 볼 수 있다.
- submodule clone을 통해 submodule 원격 저장소에서 데이터를 가져 옴
- submodule 프로젝트의 현재 상황을 바탕으로 checkout
이를 통해, submodule이 마지막 커밋 상태로 복원된다.
clone with --recurse-submodules
--recurse-submodules 옵션을 통해 위 과정을 한 번에 진행할 수 있다. git clone --recurse-submodules 커맨드를 실행한다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp$ git clone --recurse-submodules git@github.com:sirzzang/main-repo.git
Cloning into 'main-repo'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 6, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (6/6), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Total 6 (delta 0), reused 6 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (6/6), done.
Submodule 'submodule-repo' (git@github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo.git) registered for path 'submodule-repo'
Cloning into '/home/eraser/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Submodule path 'submodule-repo': checked out 'ea76cfc7e1e8e8d8899ec0fc53401499a9505802'
이와 같이 실행한 후 확인하면, 실행 결과를 통해 위에서 차례 차례 진행했던 일이 그대로 일어나는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- main repository clone
- main repository에서 submodule init
- main repository에서 submodule update
- clone
- checkout
Submodule을 포함한 Project Update
submodule이 업데이트되었을 때 submodule을 포함하고 있는 프로젝트는 어떻게 업데이트해야 할까.
먼저 submodule을 업데이트해 보자.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/submodule-repo$ echo "new commit" >> update.txt
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/submodule-repo$ git status
On branch master
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master'.
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
update.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/submodule-repo$ git add update.txt
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/submodule-repo$ git commit -m 'add update.txt'
[master a83002d] add update.txt
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 update.txt
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/submodule-repo$ git push origin master
Enumerating objects: 4, done.
Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done.
Delta compression using up to 8 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 285 bytes | 285.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
To github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo.git
ea76cfc..a83002d master -> master
submodule 원격 저장소의 가장 최신 커밋이 변경되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
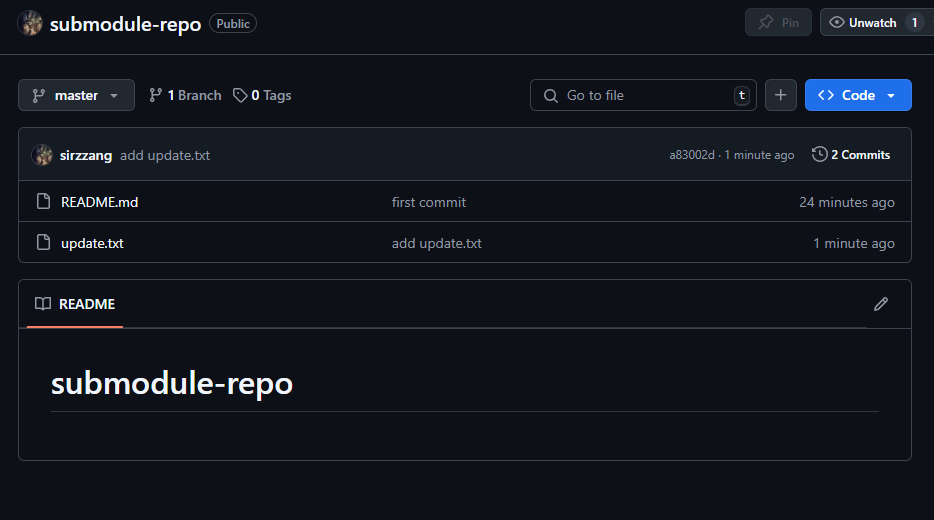
main repository에서 submodule의 상태를 확인할 경우, main repository의 submodule은 여전히 기존 커밋을 가리키고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git submodule status
ea76cfc7e1e8e8d8899ec0fc53401499a9505802 submodule-repo (heads/master)
두 프로젝트가 별개로 관리되는 것이기 때문에, 당연한 현상이다.
main repository에서 submodule의 상태를 업데이트하기 위해서는 우선 submodule 디렉토리로 이동해야 한다. 이동 후, 추적하고 있는 branch로 checkout한다.
- main repository에서 submodule을 추가하고,
git submodule update명령어를 실행해(여기에서와 같이) main repository에 submodule을 설정한 경우, submodule 로컬 저장소의 상태는Detached HEAD임 - 이 상태에서는 변경 사항 추적에 어려움이 있을 수 있기 때문에, checkout하는 것을 권장
이후 branch를 업데이트하기 위해 다음의 두 가지 단계를 거친다. 아래 두 단계는 모두 다 submodule 디렉토리로 이동 후, 추적하고 있는 branch로 checkout해 Detached HEAD 상태가 아님을 가정한다.
- branch fetch:
git fetch - branch merge:
git merge
그게 귀찮다면, main repository에서 git submodule update 커맨드를 --remote 옵션과 함께 실행하면 된다.
git submodule update --remote
submodule branch checkout
main repository의 submodule 디렉토리로 이동해, 현재 상태를 확인해 보자.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo$ git branch
* (HEAD detached at ea76cfc)
master
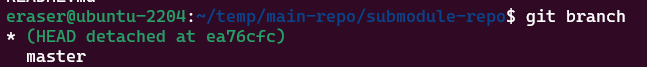
로컬 main repository의 submodule을 설정할 때, main repository의 당시 시점 기준 snapshot에 박혀 있는 submodule의 커밋 정보를 바탕으로 checkout하여 설정하게 된다. 따라서 submodule 디렉토리는 해당 커밋을 바라 보고 있는 상태로 남는다. 특정 브랜치를 보고 있는 게 아니기 때문에, Detached HEAD가 된다.
- Detached HEAD: Git이 브랜치가 아니라, 커밋을 직접적으로 가리키고 있는 상태
이 상태라면, submodule 디렉토리 안에는 변경 내용을 추적하는 브랜치가 없게 된다. 따라서 이후에 git submodule update 커맨드를 실행했을 때, 혹시라도 main repository 내 submodule에서 작업을 진행하게 된다면, 해당 작업 내용을 잃어 버릴 수 있게 된다.
그러므로, 아래와 같이 submodule에서 추적하고 싶은 브랜치로 checkout하자.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo$ git checkout master
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo$ git branch
* master
fetch
이후 submodule 디렉토리의 브랜치를 fetch한다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo$ git fetch
remote: Enumerating objects: 4, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), 265 bytes | 132.00 KiB/s, done.
From github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo
ea76cfc..a83002d master -> origin/master
merge
추적하고자 하는 submodule 원격 branch를 merge한다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo/submodule-repo$ git merge origin/master
Updating ea76cfc..a83002d
Fast-forward
update.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 update.txt
이후 main repository에서 git status를 통해 repository 상태를 확인할 경우, submodule 디렉토리에 대한 변경 사항이 발생한 것을 확인할 수 있다. 역시나, 디렉토리 하나가 통째로 변경 사항으로 취급된다.
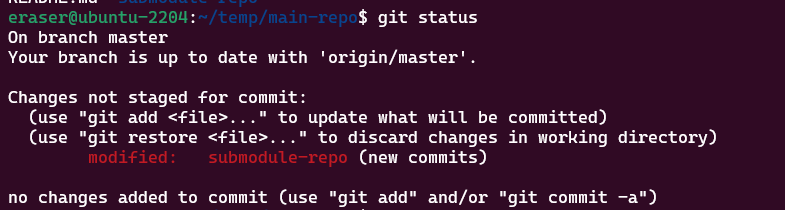
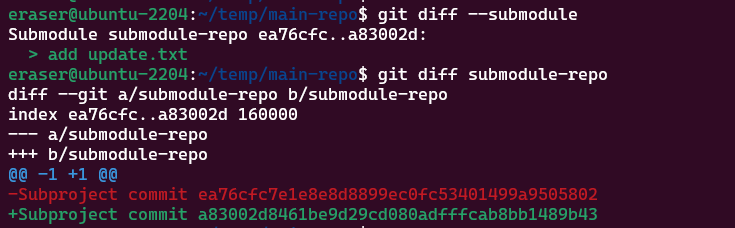
main repository에서도 변경 사항 추적을 위해 커밋을 생성하고, 원격 저장소로 푸시한다.
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo$ git add .
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/main-repo$ git commit -m 'apply submodule update'
[master a661bc9] apply submodule update
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
update with --remote
위의 과정을 진행하는 것이 너무 번거롭다면, main repository에서 --remote 옵션을 주어 git submodule update 커맨드를 실행하면 된다. 생각하는 모든 것은 다 있기 때문에
eraser@ubuntu-2204:~/temp/submodule-test/main-repo$ git submodule update --remote
remote: Enumerating objects: 4, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), 265 bytes | 265.00 KiB/s, done.
From github.com:sirzzang/submodule-repo
ea76cfc..a83002d master -> origin/master
Submodule path 'submodule-repo': checked out 'a83002d8461be9d29cd080adfffcab8bb1489b43'
submodule 최신 커밋 상태로 checkout되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
기타
추적할 브랜치를 특정하고 싶을 때
submodule 제거
활용 예
라이브러리 프로젝트
민감 정보 관리
.env, config 등으로 관리하던 민감 정보를 submodule로 관리할 수 있다. 복수의 프로젝트에서 공통으로 사용하는 여러 상수나, 환경 설정 정보 등을 분리할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 버전 관리도 되고, 접근 권한도 관리할 수 있다. 라이브러리 코드 관리에만 사용하는 방법을 생각했는데, 신박한 활용 방법인 듯 하다.


댓글남기기