[Kubernetes] Cluster: Kubespray를 이용해 클러스터 구성하기 - 3.3.3. cluster.yml - internal_facts.yml
서종호(가시다)님의 On-Premise K8s Hands-on Study 4주차 학습 내용을 기반으로 합니다.
TL;DR
이번 글에서는 cluster.yml의 두 번째 단계인 internal_facts.yml을 분석한다.
- bootstrap_os 롤: OS 감지 후 배포판별 태스크 분기 실행
- OS 감지 로직:
/etc/os-release파싱 → YAML 앵커로 vars/tasks include - Gather facts: 네트워크/하드웨어 fact 선별 수집으로 이후 플레이 최적화
전체 흐름에서의 위치
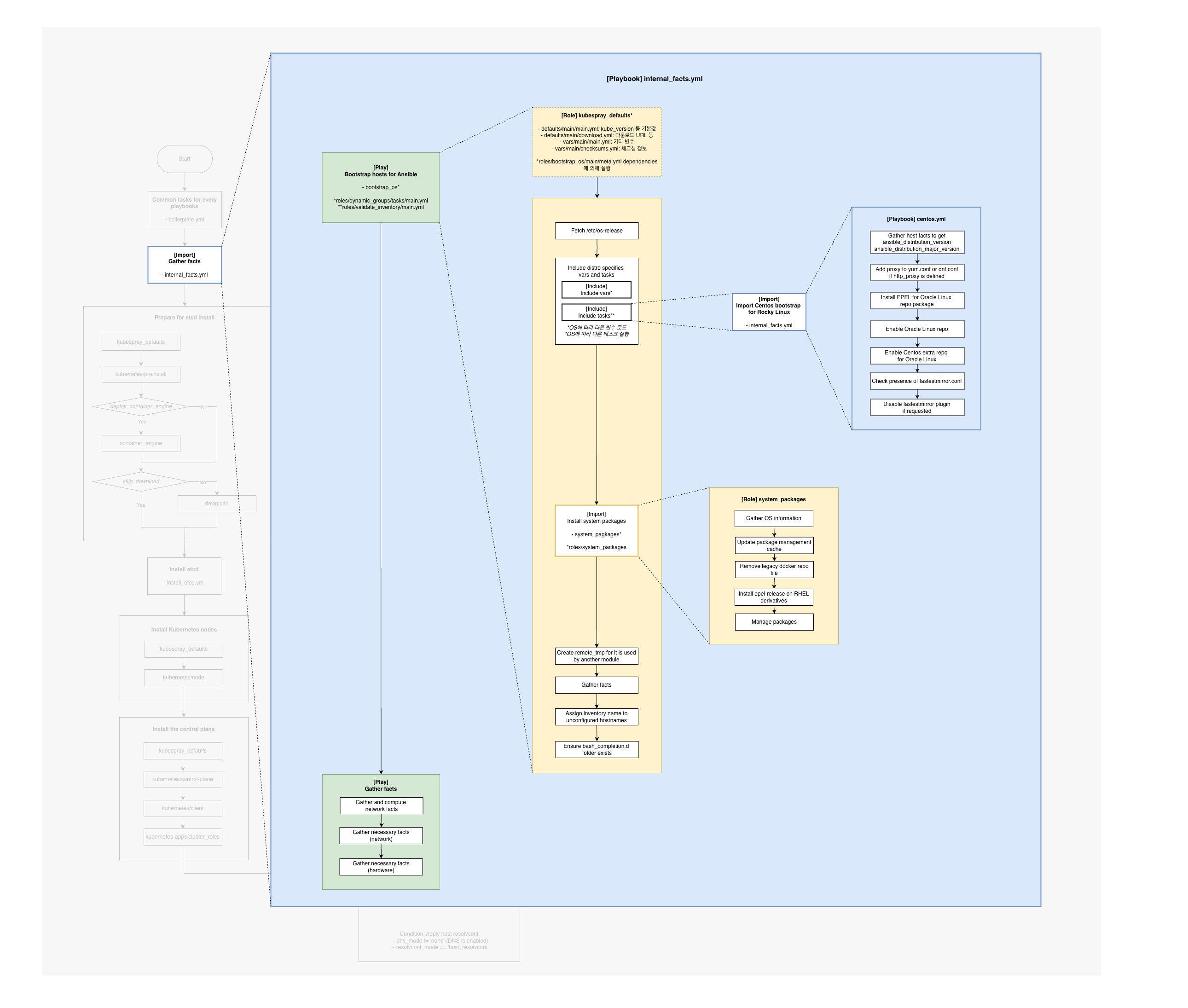
internal_facts.yml은 cluster.yml에서 두 번째로 실행되는 플레이북으로, OS 부트스트랩과 fact 수집을 수행한다.
# cluster.yml
- name: Common tasks for every playbooks
import_playbook: boilerplate.yml
- name: Bootstrap and load facts
import_playbook: internal_facts.yml # ← 두 번째 실행
internal_facts.yml 구조
---
- name: Bootstrap hosts for Ansible
hosts: k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr
strategy: linear
any_errors_fatal: "{{ any_errors_fatal | default(true) }}"
gather_facts: false
environment: "{{ proxy_disable_env }}"
roles:
- { role: bootstrap_os, tags: bootstrap_os}
- name: Gather facts
hosts: k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr
gather_facts: false
tags: always
tasks:
- name: Gather and compute network facts
import_role:
name: network_facts
- name: Gather minimal facts
setup:
gather_subset: '!all'
- name: Gather necessary facts (network)
setup:
gather_subset: '!all,!min,network'
filter: "ansible_*_ipv[46]*"
- name: Gather necessary facts (hardware)
setup:
gather_subset: '!all,!min,hardware'
filter: "ansible_*total_mb"
| 플레이 | 대상 | 역할 |
|---|---|---|
| Bootstrap hosts for Ansible | k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr | OS 부트스트랩, 패키지 설치 |
| Gather facts | k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr | 네트워크/하드웨어 fact 수집 |
1. Bootstrap hosts for Ansible
플레이 설정 분석
- name: Bootstrap hosts for Ansible
hosts: k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr
strategy: linear
any_errors_fatal: "{{ any_errors_fatal | default(true) }}"
gather_facts: false
environment: "{{ proxy_disable_env }}"
roles:
- { role: bootstrap_os, tags: bootstrap_os}
| 설정 | 값 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
hosts |
k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr |
클러스터의 모든 노드 |
strategy |
linear |
호스트별 순차 실행 (기본값) |
any_errors_fatal |
true |
하나라도 실패하면 전체 중단 |
gather_facts |
false |
자동 fact 수집 비활성화 |
bootstrap_os 롤 구조
roles/bootstrap_os/
├── defaults
│ └── main.yml
├── files
│ └── bootstrap.sh
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
├── meta
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ ├── main.yml # 메인 진입점
│ ├── rocky.yml # Rocky Linux
│ ├── centos.yml # CentOS/RHEL 계열
│ ├── ubuntu.yml # Ubuntu
│ ├── debian.yml # Debian
│ ├── fedora.yml # Fedora
│ └── ... # 기타 OS
└── vars
├── fedora-coreos.yml
└── flatcar.yml
왜 파일이 이렇게 많은가?
OS별 분기 처리를 위해 배포판마다 별도 태스크 파일이 존재한다:
tasks/
├── rocky.yml ← Rocky Linux
├── centos.yml ← CentOS
├── ubuntu.yml ← Ubuntu
├── debian.yml ← Debian
├── fedora.yml ← Fedora
└── ...
tasks/main.yml에서 OS를 감지하고, 해당하는 파일을 자동으로 include한다.
롤 실행 순서
| 순서 | 파일 | 역할 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | meta/main.yml | 의존성 (kubespray_defaults 변수 로드) |
| 2 | tasks/main.yml | 메인 진입점 |
| 3 | tasks/rocky.yml | Rocky Linux용 (OS별 분기) |
| 4 | defaults/main.yml | 기본 변수 |
| 5 | handlers/main.yml | 핸들러 |
tasks/main.yml 분석
OS 정보 수집
- name: Fetch /etc/os-release
raw: cat /etc/os-release
register: os_release
changed_when: false
check_mode: false
| 설정 | 설명 |
|---|---|
raw |
Python 없이도 실행 가능한 원시 명령 |
register |
결과를 os_release 변수에 저장 |
changed_when: false |
항상 “changed” 아님 (읽기만 하므로) |
check_mode: false |
--check 모드에서도 실행 |
OS별 vars/tasks include
- name: Include distro specifics vars and tasks
vars:
os_release_dict: "{{ os_release.stdout_lines | select('regex', '^.+=.*$') |
map('regex_replace', '\"', '') |
map('split', '=') | community.general.dict }}"
block:
- name: Include vars
include_vars: "{{ item }}"
tags:
- facts
with_first_found:
- files: &search_files
- "{{ os_release_dict['ID'] }}-{{ os_release_dict['VARIANT_ID'] }}.yml"
- "{{ os_release_dict['ID'] }}.yml"
paths:
- vars/
skip: true
- name: Include tasks
include_tasks: "{{ included_tasks_file }}"
with_first_found:
- files: *search_files
skip: true
loop_control:
loop_var: included_tasks_file
/etc/os-release 파싱 과정
os_release_dict 변수가 어떻게 만들어지는지 단계별로 살펴보자:
| 필터 | 동작 | 결과 |
|---|---|---|
os_release.stdout_lines |
줄 단위 리스트 | ["NAME=\"Rocky Linux\"", "ID=rocky", ...] |
select('regex', '^.+=.*$') |
KEY=VALUE 형태만 선택 | ["NAME=\"Rocky Linux\"", "ID=rocky", ...] |
map('regex_replace', '\"', '') |
따옴표 제거 | ["NAME=Rocky Linux", "ID=rocky", ...] |
map('split', '=') |
=로 분리 | [["NAME", "Rocky Linux"], ["ID", "rocky"], ...] |
community.general.dict |
딕셔너리로 변환 | {"NAME": "Rocky Linux", "ID": "rocky", ...} |
최종 결과:
os_release_dict = {
"NAME": "Rocky Linux",
"ID": "rocky",
"VERSION_ID": "10.0",
...
}
YAML 앵커로 코드 재사용
- files: &search_files # ← 앵커 정의 (이름: search_files)
- "{{ os_release_dict['ID'] }}-{{ os_release_dict['VARIANT_ID'] }}.yml"
- "{{ os_release_dict['ID'] }}.yml"
- files: *search_files # ← 앵커 참조 (같은 파일 목록 재사용)
&search_files로 정의하고 *search_files로 재사용해서 중복 코드를 방지한다.
with_first_found 동작
| 라인 | 설명 |
|---|---|
with_first_found: |
파일 목록 중 첫 번째로 찾은 것만 사용 |
"{{ os_release_dict['ID'] }}-{{ os_release_dict['VARIANT_ID'] }}.yml" |
예: rocky-server.yml |
"{{ os_release_dict['ID'] }}.yml" |
예: rocky.yml |
paths: [vars/] |
vars/ 또는 tasks/ 디렉토리에서 검색 |
skip: true |
파일 없어도 에러 안 남 |
block을 사용하는 이유
- name: Include distro specifics vars and tasks
vars:
os_release_dict: "{{ ... }}" # ← 이 변수를 block 안의 모든 task에서 공유
block:
- name: Include vars # ← os_release_dict 사용 가능
- name: Include tasks # ← os_release_dict 사용 가능
| 이유 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 변수 공유 | os_release_dict를 두 태스크에서 공유 |
| 논리적 그룹화 | OS별 vars, tasks include를 하나의 작업 단위로 묶음 |
Rocky Linux 동작 예시
실습 환경(Rocky Linux 10)의 /etc/os-release:
NAME="Rocky Linux"
VERSION="10.0 (Red Quartz)"
ID="rocky"
ID_LIKE="rhel centos fedora"
VERSION_ID="10.0"
PLATFORM_ID="platform:el10"
PRETTY_NAME="Rocky Linux 10.0 (Red Quartz)"
Include는 아래와 같이 동작한다:
vars/rocky-.yml찾기 → 없음 (VARIANT_ID 비어있음)vars/rocky.yml찾기 → 없음skip: true라서 그냥 넘어감tasks/rocky-.yml찾기 → 없음tasks/rocky.yml찾기 → 있음!tasks/rocky.yml실행
참고: 이후 내용은 Rocky Linux 10 실습 환경 기준이다. 실행되는 OS에 따라 include되는 태스크 파일이 다르다. Ubuntu는
tasks/ubuntu.yml, Debian은tasks/debian.yml이 실행된다.
tasks/rocky.yml
---
- name: Import Centos boostrap for Rocky Linux
import_tasks: centos.yml
Rocky Linux는 CentOS 호환이므로 centos.yml을 import한다.
tasks/centos.yml 주요 내용
---
- name: Gather host facts to get ansible_distribution_version
setup:
gather_subset: '!all'
filter: ansible_distribution_*version
- name: Add proxy to dnf.conf if http_proxy is defined
community.general.ini_file:
path: "{{ ((ansible_distribution_major_version | int) < 8) |
ternary('/etc/yum.conf', '/etc/dnf/dnf.conf') }}"
section: main
option: proxy
value: "{{ http_proxy | default(omit) }}"
state: "{{ http_proxy | default(False) | ternary('present', 'absent') }}"
when: not skip_http_proxy_on_os_packages
- name: Disable fastestmirror plugin if requested
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/fastestmirror.conf
regexp: "^enabled=.*"
line: "enabled=0"
when:
- fastestmirror.stat.exists
- not centos_fastestmirror_enabled
| 태스크 | 역할 |
|---|---|
| Gather host facts | 배포판 버전 정보 수집 |
| Add proxy to dnf.conf | 프록시 환경 설정 |
| Disable fastestmirror | 미러 선택 플러그인 비활성화 (속도 개선) |
나머지 tasks/main.yml 태스크
- name: Install system packages
import_role:
name: system_packages
tags:
- system-packages
- name: Create remote_tmp for it is used by another module
file:
path: "{{ ansible_remote_tmp | default('~/.ansible/tmp') }}"
state: directory
mode: "0700"
- name: Gather facts
setup:
gather_subset: '!all'
filter: ansible_*
- name: Assign inventory name to unconfigured hostnames
hostname:
name: "{{ inventory_hostname }}"
when: override_system_hostname
- name: Ensure bash_completion.d folder exists
file:
name: /etc/bash_completion.d/
state: directory
owner: root
group: root
mode: "0755"
| 태스크 | 역할 |
|---|---|
| Install system packages | 필수 시스템 패키지 설치 |
| Create remote_tmp | Ansible 임시 디렉토리 생성 |
| Gather facts | 기본 fact 수집 |
| Assign inventory name | 호스트명 설정 |
| Ensure bash_completion.d | bash 자동완성 디렉토리 생성 |
2. Gather facts
플레이 구조
- name: Gather facts
hosts: k8s_cluster:etcd:calico_rr
gather_facts: false
tags: always
tasks:
- name: Gather and compute network facts
import_role:
name: network_facts
- name: Gather minimal facts
setup:
gather_subset: '!all'
- name: Gather necessary facts (network)
setup:
gather_subset: '!all,!min,network'
filter: "ansible_*_ipv[46]*"
- name: Gather necessary facts (hardware)
setup:
gather_subset: '!all,!min,hardware'
filter: "ansible_*total_mb"
왜 여기서 fact를 수집하는가?
이 단계에서 필요한 fact만 미리 수집하면, 이후 플레이들은 gather_facts: false로 설정해도 된다.
| 이유 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 성능 | 매번 전체 fact 수집하면 느림 (특히 노드 많을 때) |
| 효율 | 필요한 것만 한 번에 수집 |
| 일관성 | 모든 호스트에서 동일한 fact 상태 유지 |
수집되는 fact
Kubernetes 설치에 꼭 필요한 정보만 선별하여 수집한다.
| 카테고리 | 변수 | 용도 |
|---|---|---|
| 네트워크 | ansible_default_ipv4 |
기본 IPv4 주소 |
| 네트워크 | ansible_default_ipv6 |
기본 IPv6 주소 |
| 네트워크 | ansible_all_ipv4_addresses |
모든 IPv4 주소 |
| 네트워크 | ansible_all_ipv6_addresses |
모든 IPv6 주소 |
| 하드웨어 | ansible_memtotal_mb |
전체 메모리 (MB) |
| 하드웨어 | ansible_swaptotal_mb |
전체 스왑 (MB) |
setup 모듈 옵션
- name: Gather necessary facts (network)
setup:
gather_subset: '!all,!min,network'
filter: "ansible_*_ipv[46]*"
| 옵션 | 값 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
gather_subset |
'!all,!min,network' |
전체/최소 제외, 네트워크만 수집 |
filter |
"ansible_*_ipv[46]*" |
IPv4/IPv6 관련 변수만 필터링 |
실행 로그 분석
실제 ansible-playbook cluster.yml 실행 시 internal_facts.yml 부분의 로그를 분석한다.
Bootstrap hosts for Ansible
OS 정보 수집
PLAY [Bootstrap hosts for Ansible] *********************************************
TASK [bootstrap_os : Fetch /etc/os-release] ************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr] => {"changed": false, "rc": 0, ...
"stdout_lines": ["NAME=\"Rocky Linux\"", "VERSION=\"10.0 (Red Quartz)\"",
"ID=\"rocky\"", "ID_LIKE=\"rhel centos fedora\"", ...]}
raw모듈로/etc/os-release내용을 가져옴stdout_lines에 OS 정보가 배열로 저장됨- 이 정보로
os_release_dict딕셔너리 생성
OS별 태스크 include
TASK [bootstrap_os : Include tasks] ********************************************
included: /root/kubespray/roles/bootstrap_os/tasks/rocky.yml for k8s-ctr
=> (item=/root/kubespray/roles/bootstrap_os/tasks/rocky.yml)
with_first_found로tasks/rocky.yml찾음- Rocky Linux용 태스크 파일이 include됨
CentOS 호환 태스크 실행
TASK [bootstrap_os : Gather host facts to get ansible_distribution_version ...] ***
ok: [k8s-ctr]
TASK [bootstrap_os : Add proxy to yum.conf or dnf.conf if http_proxy is defined] ***
ok: [k8s-ctr] => {"changed": false, ... "path": "/etc/dnf/dnf.conf", ...}
TASK [bootstrap_os : Check presence of fastestmirror.conf] *********************
ok: [k8s-ctr] => {"changed": false, "stat": {"exists": false}}
rocky.yml→centos.ymlimport로 CentOS 호환 태스크 실행- Rocky 10은 dnf 사용 (
/etc/dnf/dnf.conf) fastestmirror.conf없음 (Rocky 10에서는 미사용)
시스템 패키지 설치
TASK [system_packages : Manage packages] ***************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr] => (item=remove) => {"changed": false, ...}
changed: [k8s-ctr] => (item=install) => {"changed": true, ...
"results": ["Installed: conntrack-tools-1.4.8-3.el10.aarch64",
"Installed: socat-1.7.4.4-8.el10.aarch64", ...]}
remove: 불필요한 패키지 제거 (systemd-timesyncd 등)install: Kubernetes 필수 패키지 설치conntrack-tools: 네트워크 연결 추적socat: 소켓 통신 (kubectl port-forward 등에 필요)
호스트명 설정
TASK [bootstrap_os : Assign inventory name to unconfigured hostnames ...] ***
changed: [k8s-ctr] => {"changed": true, "name": "k8s-ctr",
"ansible_facts": {"ansible_hostname": "k8s-ctr", "ansible_fqdn": "k8s-ctr", ...}}
inventory_hostname으로 시스템 호스트명 설정changed: true- 호스트명이 실제로 변경됨
Gather facts
네트워크 fact 수집
PLAY [Gather facts] ************************************************************
TASK [network_facts : Gather ansible_default_ipv4] *****************************
ok: [k8s-ctr]
TASK [network_facts : Set fallback_ip] *****************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr] => {"ansible_facts": {"fallback_ip": "10.0.2.15"}, "changed": false}
TASK [network_facts : Set main access ip ...] **********************************
ok: [k8s-ctr] => {"ansible_facts": {"main_access_ip": "192.168.10.10"}, "changed": false}
TASK [network_facts : Set main ip ...] *****************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr] => {"ansible_facts": {"main_ip": "192.168.10.10"}, "changed": false}
fallback_ip: NAT 인터페이스 IP (10.0.2.15)main_access_ip,main_ip: 인벤토리에 정의한 IP (192.168.10.10)- 이후 플레이에서 노드 간 통신에
main_ip사용
최소 fact 및 필터링된 fact 수집
TASK [Gather minimal facts] ****************************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr]
TASK [Gather necessary facts (network)] ****************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr]
TASK [Gather necessary facts (hardware)] ***************************************
ok: [k8s-ctr]
gather_subset과filter로 필요한 fact만 선별 수집- 전체 fact 수집 대비 빠르고 효율적
결과
internal_facts.yml의 역할을 정리하면 다음과 같다:
| 단계 | 플레이 | 역할 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bootstrap hosts | OS 감지, 배포판별 설정, 패키지 설치 |
| 2 | Gather facts | 네트워크/하드웨어 fact 선별 수집 |
internal_facts.yml은 클러스터 노드의 OS 환경을 준비하고, 이후 플레이에서 사용할 fact를 미리 수집하는 역할을 한다. 이 덕분에 이후 플레이들은 gather_facts: false로 설정해 성능을 최적화할 수 있다.
다음 글에서는 클러스터 노드 준비를 담당하는 Prepare for etcd install 플레이를 분석한다.


댓글남기기